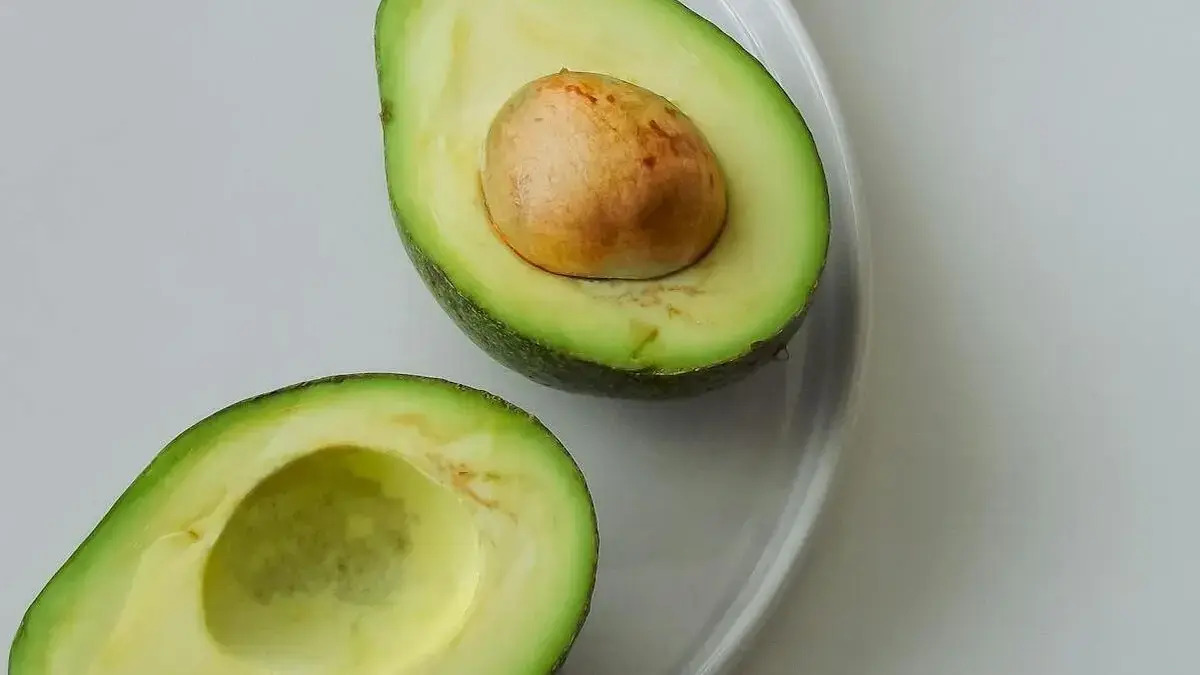
Avocado has earned its reputation as a “superfruit” for good reason. Beyond its creamy texture and unique flavor, this fruit is packed with nutrients that support heart health, eye health, digestion, and overall wellness. From monounsaturated fats to essential vitamins and antioxidants, avocado offers a remarkable combination of compounds that make it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. This article explores the science backed health benefits of avocado, practical ways to include it in your diet, and tips to maximize its nutritional potential.
Nutritional Profile of Avocado
A single medium avocado (about 150 grams) contains,
• Calories: 240
• Total Fat: 22 g (mostly heart-healthy monounsaturated fats)
• Carbohydrates: 12 g
• Fiber: 10 g
• Protein: 3 g
• Potassium: 708 mg (more than a banana)
• Vitamins: Vitamin K, Vitamin E, Vitamin C, several B vitamins including folate
• Antioxidants: Lutein, zeaxanthin, and other carotenoids
Avocado’s high monounsaturated fat content helps improve cholesterol levels, while its fiber supports healthy digestion and satiety. Its rich potassium content helps regulate blood pressure, making it especially beneficial for heart health.
Heart Health Benefits
Avocado is widely recognized for its heart-friendly nutrients. The monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, help lower LDL (bad cholesterol) while maintaining or even increasing HDL (good cholesterol). This improved cholesterol balance reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
Potassium in avocado plays a key role in maintaining healthy blood pressure. Diets rich in potassium can counteract sodium’s negative effects, reducing strain on blood vessels and lowering the risk of stroke and heart attack.
Additionally, antioxidants such as vitamin E and carotenoids protect heart cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, common contributors to cardiovascular disease.
Eye Health Support
Avocado contains lutein and zeaxanthin, two carotenoids concentrated in the retina. These act as antioxidants, protecting the eyes from harmful blue light and oxidative damage. Regular intake of lutein and zeaxanthin rich foods is linked to a lower risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts.
Pairing avocado with vegetables like spinach, carrots, or tomatoes can boost absorption of fat-soluble nutrients, including beta carotene and vitamin E, further supporting eye health.
Digestive Health and Satiety
Avocado is a fiber powerhouse, offering both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber helps regulate blood sugar by slowing digestion, while insoluble fiber promotes regular bowel movements and gut health.
The combination of fiber and healthy fats also increases satiety, helping control appetite and supporting weight management. Unlike sugary snacks or refined carbs, avocado provides nutrient dense calories that keep you full without spiking blood sugar levels.
Anti Inflammatory and Immune Benefits Chronic inflammation is linked to many health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. Avocados contain bioactive compounds such as phytosterols, polyhydroxylated fatty alcohols, and carotenoids, which exhibit anti-inflammatory effects.
Vitamin C and E in avocado act as antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals and enhancing immune function, supporting long-term wellness.
Skin and Hair Health
Avocado’s healthy fats, vitamin E, and carotenoids support skin and hair health. Monounsaturated fats maintain cell membrane integrity, keeping skin hydrated and flexible. Vitamin E protects skin cells from oxidative damage caused by UV exposure, pollution, and aging.
Avocado oil is popular in skincare for its moisturizing properties, and eating avocado regularly can complement topical care by nourishing skin and hair from within.
Practical Ways to Include Avocado in Your Diet
Avocado’s creamy texture makes it versatile for many dishes,
• Spread or Toast: Mash with salt, pepper, or lemon juice and spread on whole-grain toast.
• Salads and Bowls: Add sliced or cubed avocado to salads, grain bowls, or vegetable stir-fries.
• Smoothies: Blend with fruits like banana or berries for a creamy, nutrient-rich smoothie.
• Guacamole: Mix with tomatoes, onions, lime, and cilantro for a healthy dip.
• Baking Substitute: Replace butter or oil with mashed avocado in recipes to reduce saturated fat.
Portion and Storage Tips
Avocado is nutrient dense but calorie-rich. One medium avocado per day is generally safe for most adults. To prevent browning, store cut avocado with a squeeze of lemon or lime juice in an airtight container.
Ripe avocados yield slightly to gentle pressure. If unripe, keep them at room temperature until soft. For longer storage, freeze mashed avocado with a bit of lemon juice.
Conclusion
Avocado is more than a trendy food, it is a nutrient dense fruit with scientifically backed benefits for heart health, digestion, eye health, immunity, and skin and hair wellness. Its combination of monounsaturated fats, fiber, potassium, and antioxidants makes it a versatile and valuable addition to any diet. Including avocado in daily meals helps you feel full, supports long term health, and enhances nutrient absorption from other foods.
Whether mashed, sliced, or blended, avocado proves that creamy, wholesome goodness can go a long way for your health.
(FAQs)
1. Is avocado safe for people with high cholesterol?
Yes, its monounsaturated fats help lower LDL cholesterol and support heart health.
2. Can I eat avocado daily?
Yes, one medium avocado per day is safe for most adults.
3. Does avocado help with weight management?
Yes, the fiber and healthy fats promote satiety and prevent overeating.
4. Can children eat avocado?
Yes, its creamy texture makes it safe and nutritious for infants and children.
5. Is avocado good for skin and hair?
Yes, vitamins E and C, along with healthy fats, help maintain hydration, elasticity, and shine.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet or managing medical conditions.
Call to Action
Enjoyed learning about avocado benefits? Add this superfruit to your daily meals and experience its heart, gut, and skin health advantages. Share this article with friends and follow us for more evidence-based nutrition tips!
References
• Nutrition Facts, USDA: Verified nutrient composition of avocado, including fiber, potassium, and healthy fats.
• Journal of Nutrition, Evidence on monounsaturated fats and cholesterol improvement.
• American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Lutein and zeaxanthin supporting eye health.
• Nutrients Journal, Fiber content in avocado and its role in satiety and blood sugar regulation.
• Frontiers in Nutrition, Anti-inflammatory compounds and immune benefits of avocado.
• Dermato Endocrinology, Role of avocado nutrients in skin and hair health.