INTRODUCTION
Have you ever heard about Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)? If you’re passionate about health and wellness or curious about how technology is transforming diabetes care, you’re in the right place.
In this article, we’ll dive into what CGMs are, how they’re changing the game for people with diabetes, and how they’re not just for diabetics anymore. Let’s get started!
WHAT ARE CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORS?
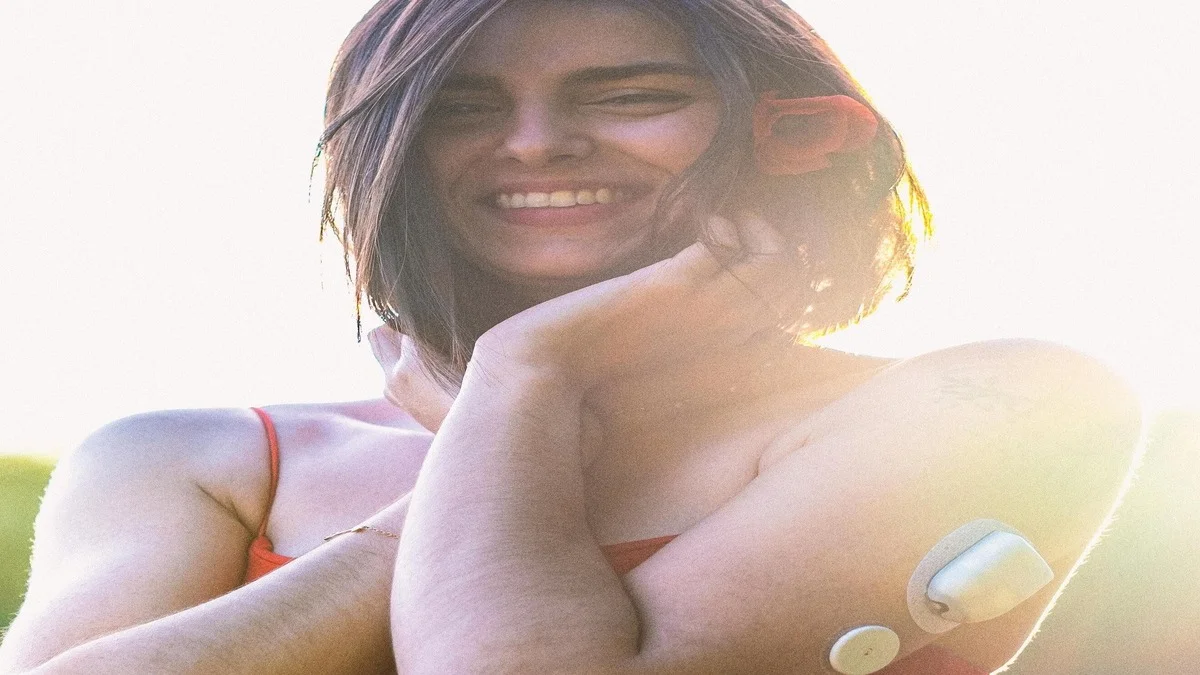
So, what exactly are CGMs? In simple terms, these innovative devices track your blood sugar levels in real time. They consist of a small sensor placed under the skin, continuously measuring glucose in the interstitial fluid.
The data is sent to a display device, like a smartphone or smartwatch, giving users an ongoing look at their glucose without the hassle of frequent finger pricks.
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), CGMs are now considered essential for diabetes management, particularly for people using insulin therapy. They allow users to detect patterns and trends that traditional finger-stick testing can miss, helping maintain more consistent glucose levels and supporting long-term health.
TRANSFORMING DIABETES CARE
Managing blood sugar is crucial for people with diabetes. Traditional finger-prick methods are often inconvenient and stressful. CGMs change that in multiple ways:
1. Real Time Monitoring
A landmark study published in Diabetes Care by Kovatchev et al. (2012) showed how continuous glucose monitoring can reduce low blood sugar episodes and improve HbA1c levels compared to traditional testing. By tracking glucose in real-time, people can respond promptly to fluctuations and better understand how meals, exercise, or medications affect their body.
2. Trends and Alerts
CGMs not only show your current glucose level but also reveal trends over time. Many devices feature alerts for dangerously high or low readings, giving users the opportunity to act quickly.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that timely alerts are especially useful in preventing overnight or exercise-induced hypoglycemia.
3. Enhanced Insights
Continuous monitoring allows for smarter diabetes management, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), CGMs provide critical data that help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions on insulin dosing, meal planning, and lifestyle adjustments.
4. Empowerment and Peace of Mind
Real-time glucose data gives users confidence and control over their condition.
The Diabetes Technology Society emphasizes that CGMs improve quality of life by offering freedom and flexibility that traditional meters cannot.
But Wait, There’s More! CGMs Aren’t Just for Diabetics
Interestingly, CGMs are proving useful for people without diabetes too. Here’s how,
1. Fitness Enthusiasts
Research published in Frontiers in Sports and Active Living (2023) highlights that keeping glucose levels stable during endurance exercise can improve energy efficiency, reduce fatigue, and speed recovery. By tracking glucose, athletes and gym-goers can tailor workouts, optimize nutrition, and boost performance.
2. Weight Management
For those focused on weight control, CGMs reveal how different foods influence blood sugar. This insight helps make healthier food choices, improve insulin sensitivity, and support sustainable weight management.
WebMD notes that detecting hidden glucose spikes, even from seemingly healthy meals, empowers better dietary decisions.
3. Health & Wellness Tracking
In the age of personalized health, CGMs fit naturally into broader biomarker tracking.
Consumer Reports highlights that non diabetic users increasingly adopt CGMs to understand metabolism, optimize energy, and make lifestyle changes that improve overall well-being.
CONCLUSION
Continuous Glucose Monitors are transforming diabetes care, giving users unprecedented control over their health. They reduce the risk of complications, improve glucose management, and provide peace of mind.
Beyond diabetes, CGMs are powerful tools for anyone looking to optimize fitness, nutrition, and metabolic health. If you’re considering a CGM, talk to a healthcare professional to find the option that best suits your needs.
Personalized health has never been more accessible, and CGMs may be the next big leap in understanding your body’s unique responses. Why not explore the possibilities?
FAQs About Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
1. What is a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM)?
A Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) is a wearable device that tracks blood sugar levels in real time. It uses a small sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid and sends data to your phone or smartwatch for continuous updates.
2. Are CGMs only for people with diabetes?
Not anymore. While originally designed for diabetes management, CGMs are now used by health conscious individuals, athletes, and wellness enthusiasts to understand how food, stress, and exercise affect their glucose levels.
3. How accurate are CGMs compared to finger prick tests?
Modern CGMs are highly accurate, with most FDA approved devices showing close correlation with traditional blood glucose meters. However, finger-prick tests may still be used occasionally for calibration or confirmation of extreme readings.
4. Can CGMs help with weight management?
Yes. By showing how your glucose levels respond to specific foods, CGMs can help you make better dietary choices, improve insulin sensitivity, and support sustainable weight management.
5. Do I need a prescription for a CGM?
In most countries, CGMs for diabetes management require a prescription from a healthcare provider. However, wellness versions designed for general health tracking are now available over the counter or online.
6. How often do you need to replace the CGM sensor?
It depends on the device. Most sensors last between 7 to 14 days, while some advanced models can last up to 6 months.
7. What are the leading brands of CGMs?
Popular FDA-approved options include the Dexcom G7, Freestyle Libre 3, and Medtronic Guardian Connect. Each offers mobile integration and customizable alert systems for glucose trends.
DISCLAIMER
This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your physician, endocrinologist, or healthcare professional before making decisions regarding diabetes management or using CGM devices.
CALL TO ACTION
• Take control of your health, one glucose reading at a time!
• Whether you’re managing diabetes or optimizing your wellness, Continuous
• Glucose Monitors offer insights that empower smarter, healthier decisions.
• Talk to your healthcare provider today about whether a CGM is right for you.
Explore more evidence-based articles on diabetes, nutrition, and metabolic health at PharmaHealths.com
REFERENCES
1. American Diabetes Association (ADA). Standards of Care in Diabetes 2025.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Diabetes and Technology: Continuous Glucose Monitoring.
3. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Diabetes.
4. Kovatchev, B. P., et al. (2012). “Continuous glucose monitoring: a global view.” Diabetes Care, 35(3), 664–668.
5. Diabetes Technology Society. Advances in Diabetes Devices and Monitoring.
6. WebMD. How Continuous Glucose Monitors Work and Who They Help.
7. Consumer Reports. Best Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) for 2025.