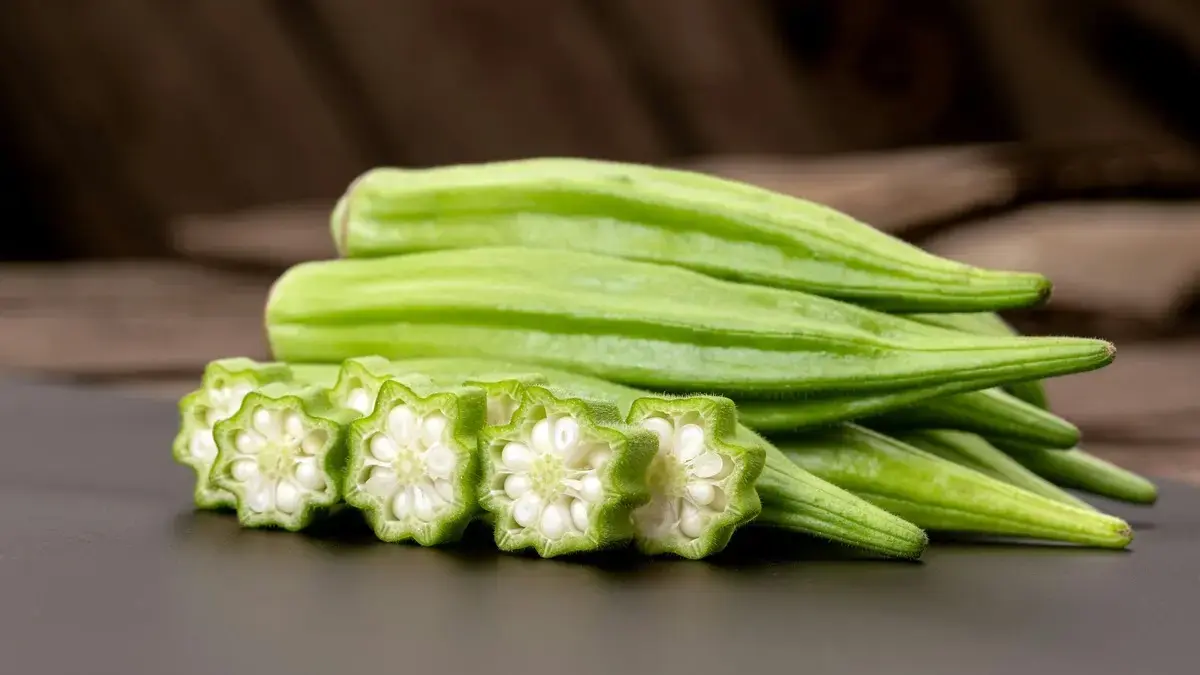
Is okra a valuable addition to a diabetic diet? Absolutely. This captivating, versatile, and nutrient-dense warm season fruit, culinarily used as a vegetable, is more than just a kitchen staple. Known as “lady’s finger,” okra is an edible seed pod celebrated as a superfood because of its abundance of essential bioactive components that support overall health and glycemic balance.
NUTRIENT RICH PROFILE OF Okra
Okra is densely packed with health-promoting nutrients, including vitamins C, K, and A, and minerals like magnesium, calcium, and folate. It also provides soluble and insoluble fibers, protein, polyphenols (catechin), flavonoids (quercetin), and polysaccharides (rhamnogalacturonan), as well as carotenoids such as lutein and zeaxanthin.
It is naturally low in fat and calories, making it an excellent dietary choice for metabolic health.
LADY’S’FINGER AND DIABETES
In this article, we’ll explore how the nutraceutical compounds in okra contribute to diabetes management and help prevent its complications.
With type 2 diabetes becoming a growing global concern, okra emerges as a promising addition to diabetic meal plans due to its bioactive compounds that may help regulate blood sugar and improve insulin function.
A LOW GLYCEMIC INDEX FOOD
Okra has a low glycemic index (GI) and is low in calories. This helps prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar, largely due to its rich dietary fiber content. Low GI foods are known to promote gradual glucose absorption and steady energy release, key factors in diabetes management.
FIBER IN OKRA AND ITS ROLE IN DIABETES
A diet high in dietary fiber supports blood sugar regulation. One cup of okra provides around 3.2 grams of fiber.
• Soluble fiber, in particular, offers several benefits in diabetes controls.
• Slows digestion, allowing for a gradual release of sugar into the bloodstream, which prevents glucose spikes.
• Promotes satiety, reducing hunger and total calorie intake, indirectly supporting weight and glucose control.
• Improves insulin sensitivity: Some studies suggest that okra may enhance the body’s response to insulin and reduce insulin resistance, thus aiding in overall glycemic regulation.
These findings are supported by research published in the American Journal of Food Science and Technology (2020) and the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry (2019), which highlight okra’s beneficial role in blood sugar management.
REDUCTION OF OXIDATIVE STRESS
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s antioxidant defenses.
In diabetes, oxidative stress plays a critical role in the development of complications such as pancreatic beta cell dysfunction, insulin resistance, diabetic neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
Okra’s high antioxidant content, especially polyphenols, flavonoids (quercetin), and vitamins A and C, helps reduce ROS levels, lower oxidative damage, and improve overall metabolic health.
These antioxidant benefits have been highlighted in studies published in Nutrients (2021) and Frontiers in Pharmacology (2020), emphasizing okra’s role in supporting metabolic health.
LOWER FASTING BLOOD SUGAR
Several experimental studies have shown that okra extract may help lower fasting blood glucose levels by delaying glucose absorption and improving insulin activity.
Animal studies published in the Journal of Pharmacy and BioAllied Sciences (2019) reported significant reductions in fasting glucose in diabetic rats treated with okra extract.
OKRA AND HbA1c LEVELS
Evidence on okra’s effect on HbA1c (a long-term marker of blood sugar control) is mixed. However, some studies suggest a mild improvement in HbA1c levels due to better glycemic control and antioxidant activity.
SUPPORTS WEIGHT MANAGEMENT
The high fiber content in okra promotes a lasting feeling of fullness, which can support weight loss by reducing calorie intake. Since obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, incorporating okra can indirectly improve metabolic health and insulin sensitivity.
HYPOLIPIDEMIC EFFECTS OF OKRA
Diabetes often coexists with high cholesterol and heart disease. Okra may improve lipid profiles through multiple mechanisms:
• Mucilage, a gel like fiber in okra, binds cholesterol in the gut and helps remove it through stool.
• Studies have shown reductions in LDL (bad cholesterol) and triglycerides after regular okra intake.
• Its antioxidant compounds prevent oxidation of cholesterol, reducing plaque buildup and supporting cardiovascular health.
These effects have been reported in research published in the Journal of Functional Foods (2020) and Nutrition Research (2018), highlighting okra’s potential benefits for heart health.
PROMOTES HEART HEALTH
Okra supports heart health by lowering inflammation and oxidative stress. Its polyphenol antioxidants help prevent atherosclerosis (arterial plaque buildup), while potassium contributes to blood pressure regulation and vascular function. Together, these effects help reduce cardiovascular risks in diabetes.
OTHER HEALTH BENEFITS OF OKRA
BONE HEALTH
Okra provides calcium and vitamin K, both essential for bone mineralization and strength, helping reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
GUT AND DIGESTIVE HEALTH
The fiber and mucilage in okra support digestive health, regulate bowel movements, and act as prebiotics that nourish beneficial gut microbes. This promotes a balanced gut microbiome, which is increasingly linked to better glucose metabolism.
COLORECTAL CANCER PREVENTION
Okra’s lectins have demonstrated anti-proliferative effects on cancer cells in some studies. Combined with its antioxidant and fiber content, okra may help lower inflammation and reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
STRONGER IMMUNE SYSTEM
Vitamin C and other antioxidants in okra strengthen immune defenses, enhancing the body’s ability to fight infections and inflammation.
PREGNANCY SUPPORT
Okra is rich in folate (vitamin B9), which prevents neural tube defects in developing babies. Its vitamin C content also enhances iron absorption, while other minerals support maternal and fetal health.
EYE HEALTH
Carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin protect the eyes from oxidative damage and help prevent age-related macular degeneration and vision loss.
PRECAUTIONS
While okra is generally safe, certain precautions are worth noting:
• Individuals with kidney stones should consult a healthcare provider before increasing okra intake due to its oxalate content.
• Its high fiber may cause mild gas or bloating in some people.
• Okra may interfere with the absorption of metformin, an important antidiabetic medication, if consumed in large amounts.
• Due to its vitamin K content, people taking warfarin should maintain consistent intake and seek medical advice.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Okra offers a range of health benefits from improving blood sugar and lipid profiles to reducing oxidative stress and supporting overall well being.
While current evidence highlights its potential in diabetes management, more large scale human studies are needed for definitive conclusions. Nonetheless, adding okra to a balanced diabetic diet is a safe, nutritious, and beneficial choice for better glycemic control and metabolic health.
DISCLAIMER
This article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. People with diabetes or other medical conditions should consult a qualified healthcare provider before making any dietary or lifestyle changes, especially if taking medications such as metformin or warfarin.
CALL TO ACTION
Incorporate okra into your meals, boiled, grilled, or stewed, and enjoy its natural power in supporting a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.
Read more : https://pharmahealths.com/vitamin-d-in-pregnancy-hypertension-diabetes/
REFERENCES:
1. Nutrients. 2021.
2. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2020.
3. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020.
4. American Journal of Food Science and Technology. 2020.
5. Journal of Pharmacy and BioAllied Sciences. 2019.